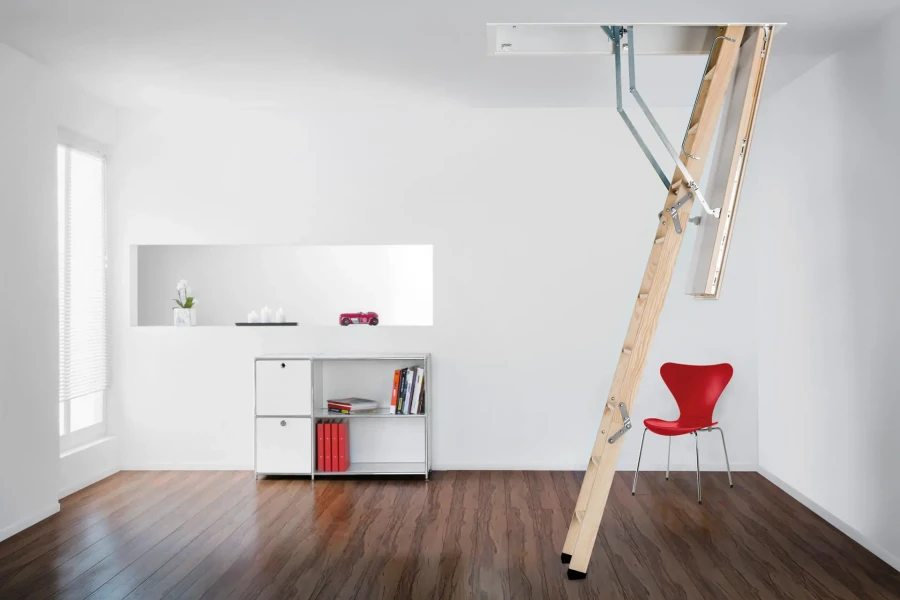
The National Audit Office has concluded that the Department of Energy and Climate Change’s (DECC) Green Deal has not achieved value for money.
The scheme, which cost taxpayers £240 million including grants to stimulate demand, has not generated additional energy savings. This is because DECC’s design and implementation did not persuade householders that energy efficiency measures are worth paying for.
The NAO report Green Deal and Energy Company Obligation also found that DECC’s design of its Energy Company Obligation (ECO) scheme to support the Green Deal added to energy suppliers’ costs of meeting their obligations. This reduced the value for money of ECO, but the Department’s information is not detailed enough to conclude by how much. Suppliers have met their obligations for saving carbon dioxide (CO2) and reducing bills.
“Improving household energy efficiency is central to government achieving its aims of providing taxpayers with secure, affordable and sustainable energy," said Amyas Morse, Head of the National Audit Office.
"The Department of Energy and Climate Change’s ambitious aim to encourage households to pay for measures looked good on paper, as it would have reduced the financial burden of improvements on all energy consumers. But in practice, its Green Deal design not only failed to deliver any meaningful benefit, it increased suppliers’ costs – and therefore energy bills – in meeting their obligations through the ECO scheme. The Department now needs to be more realistic about consumers’ and suppliers’ motivations when designing schemes in future to ensure it achieves its aims.”
The report finds that while the Department achieved its target to improve 1 million homes with the schemes, this is not a direct indicator of progress against the objective of reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. This is because different types of energy-efficiency measures save different amounts of CO2.
The schemes have saved substantially less CO2 than previous supplier obligations, mainly because of the Department’s initial focus on ‘harder-to-treat’ homes, as its analysis showed that previous schemes had absorbed demand for cheaper measures. The Department expects the measures installed through ECO up to 31 December 2015 to generate 24 megatonnes of carbon dioxide (MtCO2) savings over their lifetime, only around 30% of what the predecessor schemes achieved over similar timescales.
RIBA's Sustainability Policy Advisor Emilia Plotka added: “We need to urgently address the pending energy trilemma - energy security, climate change and fuel poverty. The Government must stop cutting corners with its lacklustre efforts and instead play a leading role through ambitious national energy efficiency programmes.
“The Green Deal and Energy Company Obligation suffered from a lack of political support and investment, and subsequently failed to offer a clear long-term vision for household energy efficiency while saving money. Reducing household energy demand remains the most cost-effective and permanent solution for saving money and meeting our legally binding commitment to reduce our carbon emissions.”
Demand for Green Deal finance has fallen well below the government’s expectations, with households only funding 1% of the measures installed through the schemes with a Green Deal loan. The schemes have not improved as many solid-walled homes, a key type of ‘harder-to-treat’ homes, as the Department initially planned. As part of changes to ECO in 2014, the Department enabled suppliers to achieve their obligations with cheaper measures, moving away from its focus on harder-to-treat properties. ECO has generated £6.2 billion of notional lifetime bill savings to 31 December 2015 in homes most likely to be occupied by fuel poor people. Beyond this, the Department cannot measure the impact of the schemes on fuel poverty.
There are significant gaps in the Department’s information on costs, which means it is unable to measure progress towards two of its objectives: to increase the efficiency with which suppliers improve the energy efficiency of ‘harder-to-treat’ houses, and to stimulate private investment. The lack of consistency in the government’s approach during the schemes could increase the long-term costs of improving household energy efficiency.
In the NAO’s accompanying investigation into DECC’s loans to the Green Deal Finance Company, also published today, it found that the Department expects that it will not recover its £25 million stakeholder loan to the finance company, plus £6 million of interest that has accrued on it. The Department based its stakeholder loan on forecasts of significant consumer demand for Green Deal loans. But demand for Green Deal finance was lower than the Department forecast from the outset, meaning the finance company could not cover its operating costs. The Department agreed a second loan worth up to £34 million in October 2014, of which the finance company has drawn down £23.5 million. The Department still expects to recover this loan in full as it will be repaid before other investors in the finance company.